Abstract
Introduction: Double-hit lymphomas (DHL), a subset of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) harboring both a MYC and BCL-2 or BCL-6 gene rearrangement, are associated with rapidly progressive disease that is often refractory to aggressive therapy. Given these poor outcomes, novel therapeutic strategies and drug combinations are desperately needed.
BCL-2 family proteins, consisting of both pro- and anti-apoptotic members, are the key mediators of the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis. BH3 profiling is a functional assay that uses synthetic peptides that mimic the BH3 domains of pro-apoptotic BCL-2 family members to measure mitochondrial "priming", or how close a cell is to its apoptotic threshold. This tool is also extremely powerful in that it can identify which anti-apoptotic proteins (i.e. BCL-2, BCL-XL, MCL-1) the cell relies on for survival. Dynamic BH3 profiling (DPB) further demonstrates whether ex vivo drug treatment enhances priming, which is an effective predictor of in vivo response, or anti-apoptotic dependencies, which can identify synergistic partners to use with BH3 mimetics such as venetoclax.
Methods: We utilized five DHL (Dogkit, DHL-4, DHL-6, OCI-Ly8, OCI-Ly18) and three non-DHL (OCI-Ly7, Toledo, and Pfeiffer) cell lines as well as two DHL patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models (available at http://www.PRoXe.org). We performed BH3 profiling in order to functionally measure overall priming as well as dependence on specific anti-apoptotic proteins. DBP was performed by treating cells with various concentrations of drugs for short intervals (16-24 hours) and subsequently performing BH3 profiling. We screened nine drugs, including conventional chemotherapy and targeted agents with suspected activity in lymphoma. Delta priming represents the change in cyctochrome c release following exposure to BH3 peptides in treated cells as compared to untreated cells. We assessed cell viability using annexin/PI staining and measured protein expression levels with immunoblotting.
Results: Baseline BH3 profiling of DHL cell lines and cell lines derived from PDX models revealed that cells rely on multiple simultaneous anti-apoptotic proteins for survival. There was a universal dependency on BCL-2, as well as in some cases, MCL-1 and BCL-XL.
Conventional chemotherapy, including doxorubicin, vincristine, mafosfamide and etoposide, had a variable effect on priming and BCL-2 dependency in DHL cell lines. Doxorubicin for example, significantly enhanced priming and BCL-2 dependency in the cell line Dogkit, but not in DHL-4 or DHL-6. In vivo treatment of two DHL PDX models with chemotherapy, including doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide, enhanced priming and dependency on the anti-apoptotic proteins, BCL-2, BCL-XL and MCL-1.
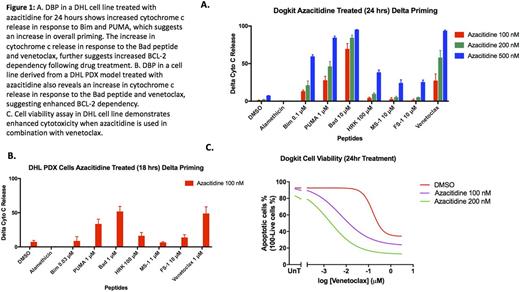
DBP was also performed using a variety of targeted agents, including lenalidomide, ibrutinib, azacitidine, bortezomib and EPZ-6438 (an EZH2 inhibitor). Interestingly, treatment with the hypomethylating agent, azacitidine, consistently enhanced priming and BCL-2 dependency across DHL cell lines and cell lines derived from PDX mice. Azacitidine treatment resulted in enhanced cell death when combined with venetoclax in cell viability assays and was associated with increased protein expression of Bim and Bad. Treatment with bortezomib also enhanced priming, though non-specifically enhanced all anti-apoptotic dependencies.
Drug treatment in non-DHL cell lines less reliably increased dependency on BCL-2 for survival, but also enhanced BCL-XL, MCL-1 and BFL-1 dependency, depending on the cell line.
Conclusions: BH3 profiling can be used to identify targetable dependencies on BCL-2, BCL-XL and MCL-1 in DHL cells lines and cells derived from DHL PDX mice. DBP additionally provides a novel approach to rationally identify drug combinations with venetoclax and other emerging inhibitors of apoptotic proteins. This strategy can identify which chemotherapy would be most efficacious for a specific cell type, especially in combination with BH3 mimetics. Furthermore, we have identified azacitidine as a promising combination therapy to use with venetoclax for the treatment of DHL. Further exploration of the role of azacitidine in combination with venetoclax for the treatment of DHL is warranted.
Davids: Celgene: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Infinity: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astra-Zeneca: Consultancy; Merck: Consultancy; InCyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Letai: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal